Notes in ML is over, welcome to the github get what you want
thanks for the sentdex again
Recurrent Neural Network
Basics
the traditional nn is [X -> Layer -> Output]
This is the RNN
the Hidden Layer is connected
Most used in NLP(Natural language processing)
RNN examples
tf.transpose(x, [1, 0, 2]): just matrix transposetranspose in numpy
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16import numpy as np
x = np.ones((1,2,3))
print(x)
print(np.transpose(x,(1,0,2)))
# [[
# [ 1\. 1\. 1.],
# [ 1\. 1\. 1.]
# ]]
#
# [
# [[ 1\. 1\. 1.]],
# [[ 1\. 1\. 1.]]
# ]tensorflow needs to transpose into (1,0,2) means 3-d -> 3-d ; 1-d -> 2-d ; 2-d -> 1-d
Convolutional Neural Network
Basics
Convolution + Pool = Hidden Layer
Fully Connected : just the same as the ordinary nn
the whole structure:
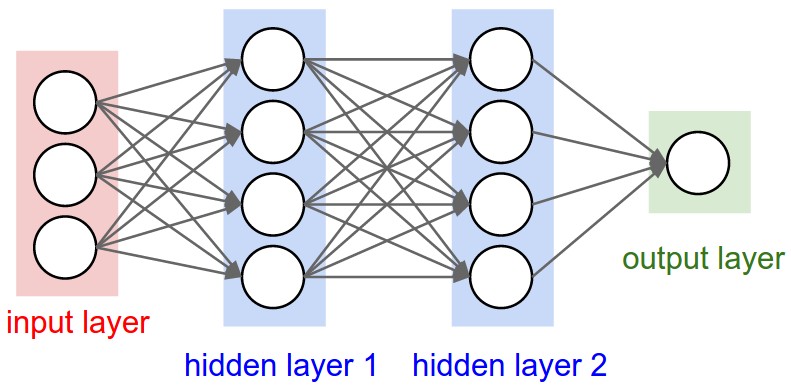
the hidden layer:
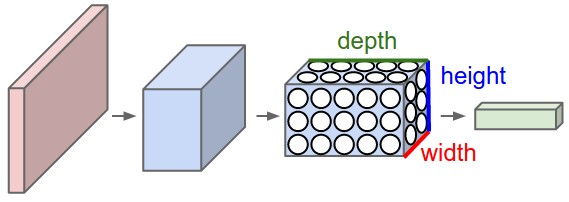
CNN examples
weights : tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([5,5,1,32]): 5 * 5 convolution ,1 input ,32 outputsweights : W_fc':tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([7*7*64,1024])): fully connected 7*7 means we just need the part of the imagestf.nn.conv2d(x, W, strides=[1,1,1,1], padding='SAME')- A list of ints. The stride of the sliding window for each dimension of input. Must be in the same order as the dimension specified with format
- padding: A string from: “SAME”, “VALID”. The type of padding algorithm to use
tf.nn.max_pool(x, ksize=[1,2,2,1], strides=[1,2,2,1], padding='SAME')- ksize: The size of the window for each dimension of the input tensor.
- strides: The stride of the sliding window for each dimension of the input tensor
fc = tf.nn.dropout(fc, keep_rate): _Dropout_- x: A tensor
- keep_prob: A scalar Tensor with the same type as x. The probability that each element is kept
TFLearn
TFlearn is a modular and transparent deep learning library built on top of Tensorflow. It was designed to provide a higher-level API to TensorFlow in order to facilitate and speed-up experimentations, while remaining fully transparent and compatible with it.
TFLearn for CNN
the example:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25X, Y, test_x, test_y = mnist.load_data(one_hot=True)
X = X.reshape([-1, 28, 28, 1])
test_x = test_x.reshape([-1, 28, 28, 1])
convnet = input_data(shape=[None, 28, 28, 1], name='input')
convnet = conv_2d(convnet, 32, 2, activation='relu')
convnet = max_pool_2d(convnet, 2)
convnet = conv_2d(convnet, 64, 2, activation='relu')
convnet = max_pool_2d(convnet, 2)
convnet = fully_connected(convnet, 1024, activation='relu')
convnet = dropout(convnet, 0.8)
convnet = fully_connected(convnet, 10, activation='softmax')
convnet = regression(convnet, optimizer='adam', learning_rate=0.01,
loss='categorical_crossentropy', name='targets')
model = tflearn.DNN(convnet)
model.fit({'input': X}, {'targets': Y}, n_epoch=10, validation_set=({'input': test_x}, {'targets': test_y}),
snapshot_step=500, show_metric=True, run_id='mnist')
model.save('tflearncnn.model')model.save('tflearncnn.model'): only save the frame but not the valuesmodel.predict([test_x[1]]): the parameters must be list
